Posts Tagged ‘Sativex’
An Appeal To Andrew Lansley
Dear Mr Lansley,
Medicinal Cannabis
I am writing to you about the urgent necessity to permit the prescribing of medicinal cannabis by doctors.
Please do not refer me to the Home Office. Its intransigent position on the subject amounts to a scandalous denial of science and cruel mistreatment of hundreds of thousands of British citizens. This is a health issue which requires your attention and care for those in pain and suffering.
There is now an overwhelming body of peer reviewed, published research that proves beyond doubt the efficacy of medicinal cannabis for the treatment of many conditions. Britain is becoming increasingly isolated as a place where patients are denied access to the medicine they need. Utterly absurd is that patients from the EU can bring medicinal cannabis into Britain under the protection of the Schengen Agreement but British residents risk prison for using exactly the same substance.
Every country in Europe except France and Britain now has some form of medicinal cannabis provision. 15 US states now permit medical marijuana on a doctor’s recommendation and Israel has a fast expanding programme. There are huge cost savings and benefits to be gained and enormous reductions in harm from side effects of poisonous pharmaceutical products.
There are already many instances in Britain where MS patients have been refused Sativex on cost grounds and so have been forced into illegal purchase or cultivation and have then been prosecuted as criminals. This is a shame and disgrace on our nation and I appeal to you to take steps to end it.
Perhaps you do not realise the transformational effect that medicinal cannabis can have on some people’s lives? Almost miraculous results are being achieved, particularly with MS, Crohn’s and fibromyalgia. People who would otherwise be trapped by pain and disability are able to lead productive lives with the help of medicinal cannabis.
Please Mr Lansley, will you arrange to meet me and a delegation of people whose lives are literally saved by the use of medicinal cannabis? This cruel and demeaning policy cannot be allowed to continue in the face of overwhelming evidence. Safe, high quality, standardised dose cannabis is now available from Bedrocan in Holland, the Dutch government’s supplier and is exported all over Europe to fill doctors’ prescriptions. How much longer must British citizens wait?
Co-ordinated action is already underway for dozens of patients to take the Home Office to judicial review for its refusal to grant import licenses for Bedrocan. This is at huge cost in public money and people’s lives. You could take steps to end this suffering now. You could enable the NHS to start making huge cost savings immediately. This issue is not going away.
CLEAR is a new team of committed professionals that is determined to bring this issue to the top of the political agenda. Please arrange to meet me and learn at first hand how much good you could do by a change of policy that is, in any case, inevitable. Don’t make those people in pain and suffering wait any longer.
I look forward to hearing from you.
Yours sincerely,
Peter Reynolds
Send a copy of this letter to your MP. Download and print here.
Legal Opportunities For Medicinal Cannabis Users
Recent developments mean that there are new opportunities to challenge the prohibition of cannabis as medicine. Now I am not a lawyer, so these ideas should be carefully discussed with your legal advisors before you even consider pursuing any of them. I may be wrong about the correct procedure, process or terminology. I am highlighting opportunities that I have identified, based on my personal experience and knowledge. Qualified legal advice is essential.
The British government’s current position on medicinal cannabis is absurd and irrational. As I understand it, those are exactly the criteria for which the process of judicial review is intended. That is one route. Another, more risky opportunity arises if you are facing prosecution or have been convicted of an offence of possession, cultivation or production. There are ideas here which you may want to consider as a defence or an appeal. However, please be very careful. If things go wrong, advancing such arguments might result in a heavier sentence, such is the cruel, oppressive and iniquitous intent of current government policy.
The Home Office is simply dishonest in its current stance saying that there “are no medicinal benefits” from cannabis. James Brokenshire, the drugs minister, cannot hide behind a lack of knowledge so he looks either more stupid or dishonest every day. David Cameron made the most dreadful, disingenuous comment about medicinal use in his Al Jazeera World View YouTube interview last week. See here. He said “That is a matter for the science and medical authorities to determine and they are free to make independent determinations about that.” That, of course, is absolute rot and Cameron should be ashamed of himself for such misinformation.
Obtain A Doctor’s Prescription For Medicinal Cannabis
There is nothing to prevent your British doctor from prescribing medicinal cannabis for you if he/she believes it is appropriate. Bedrocan BV is the official contractor to the Dutch government for the production of medicinal cannabis. Go to its website here and you will discover it has a range of products offering different proportions of cannabinoids and terpenoids for different conditions. Prescribing information is available for your doctor in exactly the same way as any other drug. All he/she has to do is select the product and write out a prescription in the normal way. Your doctor can’t get in trouble for this. There is nothing improper or unethical about it, but it is, of course, your doctor’s decision whether to do so or not.
 If your doctor isn’t prepared to help, the next best thing is to go to a doctor in Holland, Belgium, Germany, Spain or Italy, all countries where medicinal cannabis is regularly prescribed. In theory, you should be able to see a doctor in another EU country under reciprocal healthcare arrangements but if you can afford it, it may be simpler to go privately.
If your doctor isn’t prepared to help, the next best thing is to go to a doctor in Holland, Belgium, Germany, Spain or Italy, all countries where medicinal cannabis is regularly prescribed. In theory, you should be able to see a doctor in another EU country under reciprocal healthcare arrangements but if you can afford it, it may be simpler to go privately.
Another option is to go to one of the 15 US states that permit medical marijuana and obtain a doctor’s recommendation.
Once you have your prescription, you need to apply to the Home Office for a personal import licence to bring your medicine in from Holland. The licensing section on the Home Office website is here. If you obtain a licence you will also need to go through a similar process with the Dutch Bureau voor Medicinale Cannabis to obtain an export licence. The correct section of its website is here.
Of course, the reality is that the Home Office is not going to grant you a licence. You can then pursue the matter through your MP who should make representations to the minister on your behalf. You are then at the point to make an application for judical review of the Home Office’s decision.
Challenge The Government’s Interpretation Of The Schengen Agreement
The Schengen Agreement provides protection for travellers to carry their medicine with them within the EU. The crucial factor is your country of residence. See here for detailed information. Although there is no precise definition of residency, if you are resident in an EU country where medicinal cannabis is permitted, then you may bring your medicine into Britain and, believe it or not, there is no restriction on your use of it. You would be perfectly entitled to sit on the steps of Scotland Yard or even the Home Office’s Marsham Street HQ and smoke a spliff. However, if you are a UK resident, even if you have obtained your medicine on prescription abroad, you are not protected. This is clearly discriminatory under EU law and could be challenged in court. I’m not certain whether you would apply to a British court or to the European court but your solicitor would advise you on this.
Defence Or Appeal On The Grounds Of Medical Necessity
The Appeal Court disallowed a defence of medical necessity back in 2005. A petition to the House Of Lords Judicial Committee and to the European Court Of Human Rights was dismissed without any reasons given. I understand that the Appeal Court’s reasoning was that there were no proven medicinal benefits of cannabis. However, things have changed enormously since then. The MHRA approval of Sativex and the Home Office’s issue of a general licence for it are conclusive proof of medicinal value. Whatever misinformation the Home Office may promote, expert evidence would prove that Sativex is pharmacologically identical to, for instance, one of the Bedrocan products. There is also now a vast resource of peer-reviewed clinical evidence of medicinal benefits.
There is an horrendously improper judgement (R -v- David King, St Albans Crown Court), where a medicinal user was not allowed even to mention medicinal reasons to a jury on pain of imprisonment for contempt. Your lawyers would need to study this carefully. However, it is so clearly unjust that I do not believe it could be sustained.
Sativex is currently a schedule 1 controlled drug which means it has no medicinal value. As mentioned earlier, the Home Office has dealt with this temporarily by issuing a general licence for it. However, it needs to be re-scheduled and the Advisory Council On the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD) has recommended that it be placed in schedule 4. See here for the full story.
Sativex cannot be re-scheduled under its brand name and the only pharmacologically accurate way of describing it is cannabis. The ACMD left a possible escape route for the Home Office by saying that its “active” ingredients would have to be specified. GW Pharma, the makers of Sativex would say that this means an extract of THC and CBD. However, this is dishonest. Sativex contains all the 60-odd cannabinoids that occur naturally in the plant. There is no other way of describing it accurately than to call it cannabis. If Brokenshire and his cronies try to prolong this deception then they can be challenged by judicial review. The aim here is to ensure that the re-scheduling is accurate and so cannabis becomes a schedule 4 drug. This would then open up all opportunities for cannabis as medicine.
I have no doubt now that medicinal cannabis will be permitted in some form or another in Britain within the near future. We may need to force the government’s hand through litigation or, perhaps Brokenshire will be moved to another department and then the Home Office can “adjust” its position.
At present, it is a monstrous injustice, an evil and obscene scandal, that those who need cannabis as medicine are denied it. The way of politics is that a few years from now it may well all have changed and Brokenshire will be at the Ministry of Silly Walks or somewhere better suited to his talents. However it works out, what I care about is that those in pain and suffering get the relief they need. One day soon, Brokenshire will have to answer to his constituents and later to an even higher power. How he will justify his cruelty and negilgence I don’t really care but I know I wouldn’t want to be in his shoes on judgement day.
Cannabis Embarrassment At The Home Office
 The re-scheduling of Sativex, the cannabis tincture marketed by GW Pharmaceuticals is causing huge embarrassment at the Home Office.
The re-scheduling of Sativex, the cannabis tincture marketed by GW Pharmaceuticals is causing huge embarrassment at the Home Office.
Everybody’s been able to go along with the white lie up to now that Sativex is some sort of highly complex, super scientific, super medicine containing cannabinoids. True enough, GW Pharma has put millions into development and testing in order to jump through the hoops the government has demanded. At the end of the day though, all Sativex consists of is a tincture, an alcohol extract of herbal cannabis. It’s made simply by gently heating a blend of herbal cannabis in ethanol and then adding a little peppermint oil to taste.
The Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has approved Sativex for the treatment of muscle spasticity in MS. I understand that an approval for the treatment of cancer pain is expected shortly. The problem for the Home Office is that Sativex now has to be re-scheduled under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971. Cannabis is presently in schedule one as having no medicinal value. The Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD) has recommended this week that Sativex be in schedule four, alongside a variety of minor tranquilisers. However, as the ACMD says, “it will not be appropriate to refer to “Sativex”, which is a proprietary name, in any amendment to the misuse of drugs regulations, and that a suitable description of the relevant component(s) of “Sativex” will have to be scheduled.”
This is going to be tough for James Brokenshire to face up to. GW specifies that Sativex contains approximately equal proportions of THC and CBD but that’s not the whole truth. It also contains as many as 400 other chemical compounds which occur naturally in the plant including at least 85 cannabinoids (nobody is exactly sure how many cannabinoids there are or their effects). You see there’s not really any other accurate way of describing Sativex except to call it cannabis. So how can Mr Brokenshire possibly move it to schedule four? He endlessly repeats the propaganda that “there are no medicinal benefits in cannabis”.
Either Mr Brokenshire has to come clean and accept that his past position was incorrect or he has to promote some further deception.
I trust he will prove to be an honourable man.
Cannabis And Cannabinoids: Pharmacology, Medicalization And Recreational Use

By Professor Roger Pertwee
Discovery of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol
Cannabis has been used as a medicine, for religious ceremonies and recreationally for over 5000 years. Indeed, an alcohol-containing tincture of cannabis (Figure 1) was a licensed medicine in the UK until its withdrawal in the early 1970’s.
In contrast, the discovery that cannabis contains (–)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and that many of the effects experienced when cannabis is taken recreationally are caused by this ‘phytocannabinoid’ was made less than 100 years ago (Pertwee, 2006). These effects include altered mood (usually euphoria); altered perception such that colours seem brighter, music more pleasant and ‘felt time’ appears to pass more slowly than ‘clock time’; an increased desire for sweet food (the ‘munchies’); changes in thought processes; impaired memory…and eventual drowsiness. They can also include increased heart rate, a lowering of blood pressure resulting in dizziness and, at high doses, hallucinations and feelings of paranoia. There is good evidence too that Δ9-THC targets the reward centres of the brain in a manner that can lead to psychological dependence, and that abrupt termination of repeated use of cannabis or Δ9-THC can trigger a transient physical withdrawal syndrome that in abstaining recreational cannabis users most commonly includes disturbed sleep, reduced appetite, restlessness, irritability, sweating, chills, a feverish feeling and nausea.
Some Cannabinoid Pharmacology
The discovery of Δ9-THC was followed by the development of synthetic compounds capable of inducing Δ9-THC-like effects. Results obtained from pharmacological research with some of these compounds culminated in the discovery that they produce many of their central effects by activating specific sites on nerve terminals called cannabinoid CB1 receptors in a manner that influences the normal functioning of the brain (Pertwee, 2006). This finding prompted a search for molecules within our own bodies that can activate these receptors and, in 1992, led to a second major discovery – that we do indeed produce and release such molecules. The first of these ‘endocannabinoids’ to be identified was an ethanolamide of the omega-6 unsaturated fatty acid, arachidonic acid. It was named
‘anandamide’, ananda being the Sanskrit word for internal bliss. It has subsequently emerged that there is at least one other cannabinoid receptor (CB2), that there are other endocannabinoids, and that this ‘endocannabinoid system’ of receptors and endogenous receptor activators plays major roles in the control of our health and in ameliorating unwanted symptoms such as pain.
The search is now on for additional cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoids. Indeed, we have obtained evidence that ethanolamides, which are converted in our bodies from omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids that are found, for example, in fish oil, can both activate cannabinoid receptors and attack cancer cells (Brown et al., 2010).
The Medicalization Of Cannabinoids
Individual cannabinoids first entered the clinic in the 1980’s (Crowther et al., 2010). The first of these was Nabilone (Cesamet), a synthetic Δ9-THC-like compound that is used to suppress nausea and vomiting produced by cancer chemotherapy. Synthetic Δ9-THC (Marinol) was licensed soon after Nabilone for the same purpose, and subsequently as an appetite stimulant, particularly for AIDS patients. Nabilone
and Marinol were recently joined in the clinic by Sativex: in Canada (2005) for the relief of multiple sclerosis and cancer pain and in the UK (2010) to treat spasticity due to multiple sclerosis. Sativex has also received regulatory authorisation in Spain. Its main constituents are two phytocannabinoids, Δ9-THC and cannabidiol, both extracted from cannabis.
Importantly, whereas exogenously administered cannabis and individual cannabinoids such as Δ9-THC and Nabilone target all cannabinoid receptors in the body and so ‘flood’ the whole endocannabinoid system, endocannabinoids released endogenously are somewhat more selective since they seem to be released in a manner that only targets subpopulations of their receptors. Although such release is often ‘autoprotective’ it can sometimes be ‘autoimpairing’, leading for example to CB1 receptor-mediated obesity. There is, however, currently little interest in developing medicines from compounds that block CB1 receptors, as such a blockade could well also suppress CB1 receptor-mediated autoprotection. Indeed, the CB1 receptor blocking drug, Rimonabant, was recently withdrawn from the clinic because of an increased incidence of depression and suicidality in patients taking it as an anti-obesity agent.
The fact that Cesamet, Marinol and Sativex are all in the clinic is of course an indication that, as prescribed, these medicines do significantly more good than harm. Even so, there is considerable interest in developing a second generation of cannabinoid medicines that display even greater ‘benefit-torisk ratios’ (Pertwee, 2009). Possibilities include compounds that avoid the production of unwanted cannabinoid CB1 receptor-mediated effects by:
(1) Only activating cannabinoid receptors that are located outside the brain and spinal cord.
(2) Only activating cannabinoid receptors in particular tissues such as skin or spinal cord by being administered directly into these tissues.
(3) Activating cannabinoid CB2 but not cannabinoid CB1 receptors.
(4) Being administered at low doses that produce a cannabinoid receptor-mediated enhancement of the sought after effects of non-cannabinoid medicines but are insufficient to produce significant cannabinoid receptor-mediated unwanted side effects.
(5) Boosting the levels of endocannabinoids when these are being released in an ‘autoprotective’ manner, for example to relieve pain.
(6) Targeting ‘allosteric’ sites that we have discovered to be present on cannabinoid CB1 receptors in a manner that will boost the ability of autoprotectively released endocannabinoids to activate these receptors.
Cannabis: A Complex Scenario
Δ9-THC is synthesized in the cannabis plant from a nonpsychoactive precursor, Δ9-THC acid. This process can be greatly accelerated by heat which is why cannabis is usually smoked, often with tobacco, consumed in preheated food or inhaled from ‘volcano’ vaporizers that create fumes by heating cannabis without burning it or producing smoke. Other pharmacologically active phytocannabinoids can also be
formed from their acids by heating cannabis. These include the non-psychoactive yet pharmacologically active compounds, cannabidiol (CBD), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (Δ9-THCV) and cannabigerol (CBG), each of which has actual (CBD) or potential medical applications. Some of these phytocannabinoids are really ‘fighto’ cannabinoids, their presence in cannabis making it a pharmacological ‘battlefield’. Thus
we have discovered that although CB1 receptors are activated by Δ9-THC, they can be blocked by Δ9-THCV. It has also been found that CBD can oppose certain effects produced by cannabis or Δ9-THC. Indeed, whilst there is evidence that the presence of Δ9-THC in cannabis increases the risk of developing schizophrenia for certain individuals, there is also strong evidence that cannabidiol is a potential medicine for the treatment of schizophrenia. A further complication is that the relative concentrations of different phytocannabinoids are not the same in all strains of cannabis, in all parts of the same cannabis plant or in male and femalecannabis plants, the female flowering heads of sinsemilla (‘without seeds’) being particularly rich in Δ9-THC. This may have important consequences for those who take cannabis either recreationally or for the quite different purpose of self-medication, as high CBD:THC or THCV:THC ratios may lessen the risk from cannabis of developing schizophrenia or cannabis dependence…although probably also alter the perceived nature of a cannabis-induced ‘high’.
Spice
One notable recent event has been the arrival in the recreational cannabis world of herbal mixtures laced with synthetic cannabinoids (‘designer drugs’) such as JWH-018 (e.g. Spice or K2, named after the second highest mountain on earth). These little-investigated synthetic cannabinoids share the ability of Δ9-THC to activate cannabinoid CB1 receptors and hence to produce a ‘high’. Moreover, any of them that
activate these receptors more strongly than Δ9-THC will most likely produce a more intense ‘high’ and perhaps also more serious unwanted effects than usually experienced by recreational cannabis users. They probably also differ from THC in other ways. Thus, although Δ9-THC shares its ability to target cannabinoid receptors with many synthetic compounds, the additional pharmacological actions it possesses provide it with a unique ‘pharmacological fingerprint’ that distinguishes it from many of these other compounds.
Harm Minimization For Recreational Cannabis
One important challenge for the International Narcotics Control Board that monitors and implements United Nations drug control conventions is to select an optimal but workable strategy for minimizing the harm that is now being caused both to themselves and to Society by some of the many millions of people world-wide who currently take cannabis (or Spice) recreationally and also, indeed, by some of those who self-medicate with ‘street’ cannabis. For the UK, options include leaving the present law unchanged and increasing or
decreasing current penalties for the supply and/or possession of ‘street’ cannabis. It would also be advisable to develop strategies directed (i) at discouraging cannabis from being taken by adolescents or other individuals who are thought to be at particular risk from cannabis-induced harm and (ii) at providing advice (a) about combinations and levels of cannabinoids in cannabis that are thought to be the least
harmful and (b) about how to take cannabis as an inhaled unburnt vapour or in other ways that avoid the lung damage caused by smoked cannabis. It will be important that policy makers have discussions with cannabinoid pharmacologists whilst considering these and any other potential strategies for minimizing the harm caused by recreational cannabis.
Brown I, Cascio MG, Wahle KWJ, Smoum R, Mechoulam R, Ross RA, Pertwee RG and Heys SD. Cannabinoid receptor dependent and independent anti-proliferative effects of omega-3 ethanolamides in androgen receptor positive and negative prostate cancer cell lines.
Carcinogenesis 2010; 31: 1584-1591.
Crowther, SM, Reynolds, LA and Tansey, EM (eds). The Medicalization of Cannabis. Witness Seminar Transcript. Volume 40. The Wellcome Trust Centre for the History of Medicine, at UCL. 2010; http://www.ucl.ac.uk/histmed/downloads/c20th_group Pertwee RG. Cannabinoid pharmacology: the first 66 years. Br J Pharmacol 2006; 147: S163-S171. Pertwee RG. Emerging strategies for exploiting cannabinoid receptor agonists as medicines. Br J Pharmacol 2009; 156: 397-411. Professor Roger Pertwee has three degrees from the University of Oxford: MA (in biochemistry), D.Phil. (in pharmacology) and D.Sc. (in physiological sciences). He is Professor of Neuropharmacology at the University of Aberdeen, Director of Pharmacology for GW Pharmaceuticals, co-chairman of the International Union of Pharmacology (IUPHAR) Subcommittee on Cannabinoid Receptors, a co-ordinator of the British Pharmacological Society’s Special Interest Group on Cannabinoids and visiting Professor at the University of Hertfordshire. He has also served as chairman of the International Association for Cannabis as Medicine (IACM; 2005-2007) and as President of the International Cannabinoid Research Society (ICRS; 2007-2008; 1997-1998) and is currently ICRS International Secretary and a member of the IACM board of directors. He was the recipient of the 2002 Mechoulam Award “for his outstanding contributions to cannabinoid research” and in 2005 was recognized to be an “ISI Highly Cited Researcher” and hence among “the world’s most cited and influential researchers” (see Pertwee at http://isihighlycited.com/). His research has focused mainly on the pharmacology of cannabinoids. This he began in 1968 at Oxford University and continued when he moved to Aberdeen in 1974. His research has played major roles in:
• the discovery of endocannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system;
• the recent discovery that ethanolamides formed from omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids seem to be endocannabinoids;
• the gathering of evidence supporting cannabinoids for the management of multiple sclerosis;
• the discovery that tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is a phytocannabinoid;
• the pharmacological characterization of certain phytocannabinoids and of novel synthetic cannabinoids, e.g. the phytocannabinoids THCV, cannabidiol and cannabigerol, the first water-soluble cannabinoid (O-1057), the first CB1 receptorselective agonists (e.g. methanandamide), and a widely-used CB2 receptor antagonist (AM630);
• the discovery of a cannabinoid CB1 receptor allosteric site;
• the development of cannabinoid bioassays, some widely used (e.g. the “ring test”).
See also www.abdn.ac.uk/ims/staff/details.php?id=rgp
Advisory Council On The Misuse of Drugs Meeting, 18th November 2010
I attended this meeting last Thursday at Church House, just around the corner from the Houses of Parliament.
There were approximately 35 members of the council in attendance, sitting around a huge U shaped table with perhaps 20 people in the public seats. Inevitably, such a huge meeting could only touch on adminstrative matters and formalities. Clearly, most of the ACMD’s work is done in much smaller working groups. However, there was an interesting Q&A session and I was pleased to experience a council meeting. I wouldn’t recommend it for light entertainment though!
Professor Leslie Iversen was in the chair for the last time. His post and those of eight other members have been advertised and their replacements will be appointed as from 1st January 2011. These are voluntary positions with members receiving only expenses and subsistence payments for their work. They undertake an onerous and important responsibility and I commend them for their public service.
Full minutes should be available on the Home Office website here within a few weeks. However the main items of interest were:
- the ACMD’s response to the Home Office’s drug strategy consultation
- a report on anabolic steroids
- a report on the issuing of foil by drug clinics as an alternative to injection
- a report on 2-DPMP, marketed as the “Ivory Wave ” legal high
- a request to report on khat, the herbal product from East Africa that contains cathinone, the same active ingredient as mephedrone
- a request to report on cocaine use after a recent report placed Britain at the top of the European league table
Then we came to the Q&A session and, of course, yours truly had a question prepared. First though there was a large contingent of the Somalian community present appealing for the prohibition of khat.
I have to say that nothing I have heard about either mephedrone or khat has interested me or persuaded me to experiment. There were a number of emotional and passionate speeches rather than questions; one from an ex-khat addict, one from a Somalian psychiatrist and others from community members. It’s clear that khat does cause harm but it saddened me that the only solution being suggested was prohibition. I understand this as a knee jerk reaction but it won’t work. All it will do is drive use undergroud and make the problem worse. Professor Iversen himself commented that the price of khat where it has been banned is 20 times that of where it is legal. If prohibition is enacted in Britain all we will be doing is playing straight into the hands of criminal gangs yet again.
I asked the council whether there wasn’t an urgent need for it to update its advice to the government on the medicinal benefits of cannabis. I cited the recent MHRA approval of Sativex which is, of course, nothing more than a tincture of herbal cannabis. I also mentioned that Arizona had just become the 15th state in America to introduce a medical marijuana programme and that Israel has recently announced a massive increase in growing facilities and dispensaries.
I am paraphrasing here, of course, but Professor Iversen threw up his hands in horror at being asked to review cannabis again when he has already done so three times. The general view from the council seemed to be that whatever was said to government on this subject, no notice would be taken. I shall be following up my oral question with a letter to Profesor Iversen. We have to expose this Home Office lie that there are no medicinal benefits from herbal cannabis and that this is based on advice from the ACMD. It isn’t. It’s a government deception.
For me the most important part of the day was the opportunity to introduce myself in person to Professor Iversen. I thanked him for agreeing to become a founder council member of the British Medicinal Cannabis Register. He said how enthusiastic he was about the register and that he has been an advocate of medicinal cannabis since the 1990s.
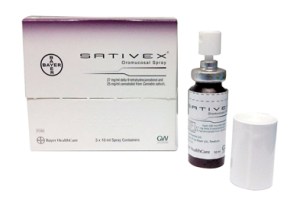
The Truth About Sativex
 Sativex is super strong, concentrated cannabis. Nothing more, nothing less.
Sativex is super strong, concentrated cannabis. Nothing more, nothing less.
GW Pharmaceuticals would have you believe that it’s a “pharmaceutical” product because according to its research that’s what patients prefer. As the GW spokesman puts it, “It’s a pharmaceutical solution, formulated with the ability to deliver a precise dose and with stringent standards of quality, safety and efficacy”.
 In fact, what GW does is grow high quality cannabis under pretty much the same conditions as most illegal growers. It uses clonal propagation to ensure consistent levels of cannabinoids. Lighting and hydroponic nutrition is computer controlled with automatic ventilation. It really is no different from the most sophisticated and efficent illegal cannabis farms. It’s a recognised and proven technology now also used by Bedrocan in Holland, the Dutch government’s exclusive medicinal cannabis grower and Gropech in California which is building a new 60,000 sq ft facility in Oakland for a crop worth $50 million per year.
In fact, what GW does is grow high quality cannabis under pretty much the same conditions as most illegal growers. It uses clonal propagation to ensure consistent levels of cannabinoids. Lighting and hydroponic nutrition is computer controlled with automatic ventilation. It really is no different from the most sophisticated and efficent illegal cannabis farms. It’s a recognised and proven technology now also used by Bedrocan in Holland, the Dutch government’s exclusive medicinal cannabis grower and Gropech in California which is building a new 60,000 sq ft facility in Oakland for a crop worth $50 million per year.
The difference between these crops from legal and illegal growers is insignificant. It’s similar to buying your tomatoes from the supermarket or the farm shop.
GW takes its high quality cannabis, chops it up and makes a tincture by heating it under pressure with CO2 and then adding ethanol to precipitate an oil. Then, with the addition of a little peppermint oil to mask the taste and some preservative, the filtered liquid is packaged into tiny little aerosol bottles. Each spray delivers 2.7mg of THC and 2.5mg of CBD. What GW doesn’t tell you that it also contains all the other 100+ cannabinoids found in the plant, each of which has its own mechanism of action and effect. It also contains flavonoids, terpines and other compounds. Everything that is found in the plant.
I applaud GW Pharmaceuticals for bringing the enormous benefits of cannabinoid therapy into the 21st century. It’s nothing new though. The medicinal value of the plant has been known and widely used for thousands of years. Only in the last century has it been demonised by lies and propaganda. It would be a mistake though to think that Sativex is anything different from the plant itself. It’s just been wrapped up in a marketing and physical package which has enabled stupid and cowardly politicians to accept it.
In fact, Sativex remains just as illegal in Britain as herbal cannabis. Even though it has received MHRA approval for use in the treatment of MS spasticity and may be prescribed by a doctor, it remains a schedule 1 drug under the Misuse Of Drugs Act. The Home Office has indicated that it intends to amend the law but has not yet done so. This means that any pharmacist who dispenses Sativex at present is guilty of exactly the same criminal offence as any street dealer in weed or hash.
The Home Office will, of course, turn a blind eye to this but not to medicinal herbal cannabis even though, in every sense, it is identical to Sativex (except that Sativex also contains alcohol and peppermint oil). The stark idiocy of British law is revealed.
Never before has there been a better example of the how the law is an ass and so are the spineless politicians who support it.