Posts Tagged ‘CBD’
Home Secretary Invites CLEAR To ‘Enter A Dialogue’ On Cannabis Law Reform.
In a letter dated 15th August 2016, Amber Rudd, the new Home Secretary, has invited CLEAR to raise “any queries and concerns” about present UK policy on cannabis. This is the first time since 2006, with Charles Clarke, that the UK cannabis campaign has had any direct contact with a serving Home Secretary. It reflects the reality, now recognised in government, that changes in cannabis policy are imminent.
In recent months, there has been a manifest and significant change in attitudes within the Home Office. We have seen this through the process of obtaining a low THC cultivation licence for our partnership with GroGlo Research and Development. The response from the drugs licensing department has been enthusiastic. There has been no difficulty with our declared purpose of producing CBD oil for sale as a food supplement and we are now in detailed discussions on our application for a high THC licence, looking towards clinical trials for a medical product for chronic pain.
As soon as Theresa May announced that Amber Rudd would be heading up the Home Office, I contacted my MP, now Sir Oliver Letwin, thanks to Cameron’s resignation honours list. Although he will not openly support our campaign, in the past year or so he has been very helpful indeed, meeting with me on roughly a monthly basis and helping me navigate through the Conservative government. He has now put me in direct contact with Ms Rudd and I will be preparing a written submission as a preliminary to a face-to-face meeting.
In accordance with CLEAR policy, our first concern is how we can enable UK residents to gain access to medicinal cannabis on a doctor’s prescription. In practice that means Bedrocan products as there is presently no other source of prescribable, consistent, high-quality, herbal cannabis. I would expect that to change very soon though. Both Canada and Israel look like potential near-future sources. GW Pharmaceuticals is undoubtedly considering entering the market and our venture with GroGlo could shift gear depending on how quickly UK policy changes.
We will also be addressing the need for wider reform and a legally regulated market for adult consumers. Although medicinal access remains the top priority, there is no doubt that more overall harm is caused by prohibition of the recreational market. It is this that creates the £6 billon per annum criminal market which is the cause of all the social harms around cannabis. This will need to be handled much more carefully as, due to nearly a century of misinformation and media scaremongering, many people still retain great fear as to what legal cannabis will mean.
The one thing that has been very lacking in the cannabis campaign is pragmatism. Most campaigners for recreational use continue to be lost in a swirl of ‘free the weed’, teenage angst, outrage, revolution and delight in being a rebellious outlaw. That was until 2011 when CLEAR introduced a new approach which has led to more engagement with government than ever before. The emergence of the United Patients Alliance and now the End Our Pain campaign has helped this but these campaigns are focused only on medicinal use
The fact is that we need to work with Theresa May’s government and the anti-Tory tribalism that many still adopt is nothing but an obstacle to reform.
In addressing Ms Rudd, our overall strategy for wider reform will be:
1. A final separation from the ridiculous ‘free the weed’ movement and ‘stoner’ groups which are incapable of understanding how they are seen and despised by wider society.
2. Differentiation between medicinal use and the more controversial legalisation for adult, recreational use.
3. Shift public attention onto scientific and medical evidence rather than the very poor standard of media reporting.
4. End the fake policy that says ‘cannabis is dangerous therefore it must be regulated’. Educate that nearly all the harms around cannabis are caused by its prohibition, not by cannabis itself.
5. Emphasise the importance of harm reduction information, education about excessive use and essential investment in treatment for those who do suffer health harms.
6. Clarify that decriminalisation is no solution and is a dangerous option that would probably increase harm. The product needs to be sold within a properly regulated environment, careful that over-regulation would support a continuing criminal market.
CLEAR and GroGlo Establish First UK Clinical Trials on Cannabis for Chronic Pain.
CLEAR has formed a partnership with the research arm of GroGlo, a UK-based manufacturer of high power, LED, horticultural grow lighting.
The plan is to grow cannabis under a Home Office licence for the production of cannabis oil, both as a dietary supplement and for the development of medical products. To begin with, a low-THC crop of industrial hemp will be planted. We will be using the finola strain, originally developed in Finland and known for its short stature and early flowering. Unlike hemp grown for fibre, finola is usually grown for seed and only reaches a height of 160 – 180 cm but we will be removing male plants before they produce pollen and cultivating the female plants to produce the maximum yield of oil from their flowering tops.
The low-THC oil will be marketed as a dietary supplement, commonly known as CBD oil. There is already a burgeoning market in the UK for CBD products, all of which is currently imported from Europe or the USA. In the USA, the CBD products market was said to be worth $85 million in 2015 so there is huge potential here at home. Aside from the benefit of being UK grown and processed, we anticipate achieving a CBD concentration of about 40%, which is higher than most products already on the market.
Cultivation will be in glasshouses supplemented with LED lighting. GroGlo already has an established glasshouse facility in the east of England. Initial trials will experiment with adjusting the LED technology to provide a changing blend of light wavelengths at different stages of plant growth. This is GroGlo’s area of expertise -combining LED lighting and plant sciences, including existing relationships with some of Europe’s top universities. Professor Mick Fuller, GroGlo’s director of plant science, will lead this research and development process.
During the R&D phase, CO2 extraction of oil will be carried out under laboratory conditions at universities in York and Nottingham which already have extensive experience of the process. Each crop will be measured for yield, cannabinoid and terpene content using high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC). Safety testing will also look for the presence of heavy metals and other contaminants. The results of testing will be fed back into cultivation and extraction processes to maximise yield and quality.
It is anticipated that the first batches of low-THC oil will be ready for market in six months. We are already in discussions with potential distributors and wholesalers. The CBD market in the UK is ripe for an effective marketing campaign which could build a very substantial business for whoever gets it right.
Once we are successfully achieving our production goals with low-THC cannabis, the same testing and development process will begin with high-THC varieties of cannabis. The aim will be to produce a range of oils extracted from single strains, selectively bred and stabilised for different THC:CBD ratios.
Professor Fuller says that GroGlo lighting products “are in use worldwide to grow a range of crops, but some 60% of sales currently come from overseas users growing cannabis for legitimate medical use.” He explains that there is an emerging market for all sorts of nutritional and medicinal plant products but cannabis shows particular promise. GW Pharmaceuticals is the only UK company to enter this market and it has become a world leader, despite the current restrictive legislation. He says: “Together with CLEAR we believe we can help bring a range of safe, high quality UK-produced cannabis products to market within a matter of two to three years.”
A key issue in the development of a successful medicinal cannabis product is the method of delivery. Smoking is not an acceptable solution as inhaling the products of combustion is an unhealthy practice but one of the great benefits of cannabis smoked as medicine is very accurate self-titration. That is the effects of inhaled cannabis are felt almost instantly and so the patient knows when they have taken enough or when they need more to achieve the required analgesic effect.
The oral mucosal spray developed for Sativex is unpopular with patients, many complain of mouth sores from its use and it was developed at least as much with the objective of deterring ‘recreational’ use of the product as with delivering the medicine effectively. It strangles the therapeutic benefits of the cannabis oil of which Sativex is composed in order to comply with the concerns of the medicines regulators about ‘diversion’ of the product into what they would term ‘misuse’. Absorption of the oil is quicker through the mucous membranes of the inside of the mouth than through the gastrointestinal system but, inevitably, some of the oil is swallowed and the pharmacology of cannabis when processed through the gut and the liver is very different.
We believe the best option is a vapouriser device and our intention is to source a ‘vape pen’ of sufficient quality to operate within clinical standards of consistency and safety. Vapourising cannabis oil avoids inhaling the products of combustion but still enables accurate self-titration of dose. A vape pen would provide a handy, convenient and very effective method of consuming medicinal cannabis. However, aside from the technology itself, initial research shows that vapour is more effectively produced when the oil is blended with either vegetable glycerin (VG) or propylene glycol (PG). Establishing the correct ratio of VG or PG to the oil is another important task.
We anticipate that clinical trials for the use of cannabis oil in treating chronic pain could start within two years. We want to compare different oils, ranging from high-CBD to equal ratios of THC:CBD and high-THC content. Prior to that we have to overcome the challenges of cultivation, oil extraction, vapouriser development and assemble the necessary research team and gain ethical approval for the trials. Recruitment for the trials will start in about 18 months time. If you wish to be considered please email ‘paintrials@clear-uk.org’ with brief details of your condition (no more than 100 words). Do not expect to hear anything for at least 12 months but your details will be passed to the research team as a potential candidate.
CLEAR is promoting this venture simply because someone needs to do something to make this happen. For all the campaigning and lobbying of MPs and ministers, at the end of the day, the plants have to be grown and the various legislative hoops have to be jumped through. We cannot wait any longer for a radical change in the law. We have to progress through the government’s regulatory regime if we want to bring real therapeutic benfit to patients.
This opportunity arises because of the vision of GroGlo’s managing director, Mike Harlington and the team of experts he has built around him. There is huge demand for legitimate medicinal cannabis products in the UK which is only going to increase with the inevitable progress towards law reform and increasing awareness of the benefits of cannabis. Together, CLEAR and GroGlo are bringing the great hope that medicinal cannabis offers closer to reality than ever before.
This Is The Future Of Cannabis. For Medicine, Nutrition And Pleasure.
One of these vape pens contains Blue Dream sativa cannabis oil, 91% THC, the other is Hindu Kush indica cannabis oil, 85% THC and the spare cartridge has the dregs of some New York City Diesel sativa, 85% THC. You can’t tell which is which to look at them but each has a distinctive flavour and effect. They’re not completely odour free but almost.
This is the future of cannabis as a consumer product. It is cleaner, neater, handier, healthier and better for you than raw herbal cannabis. Most importantly, for medicinal applications, it homogenises all the compounds into an oil of consistent quality and content meaning that dosage and effect at last becomes predictable and reliable.
I have been investigating this theory for some time but my recent trip to Colorado enabled me to conduct some practical experiments and more thoroughly understand how this idea can work. I am now convinced that this is the way forward for the cannabis industry. Once we achieve legalisation in the UK, which is inevitable, probably in about five years, these pens are how cannabis will become available as a consumer product on the high street. They are also how medicinal cannabis will be dispensed. Your doctor’s prescription will be fulfilled by a cartridge with the appropriate blend of cannabinoids which you screw onto your battery and use immediately. Batteries will also be supplied on prescription, in the same way that syringes or blood glucose meters are for diabetics.
In Colorado dispensaries these pens are already available in a choice of strains and blends. Currently, the popular products contain 250 mg of THC in a blend of cannabis oil and propylene glycol (PG), just as e-cigs contain a nicotine oil and PG.
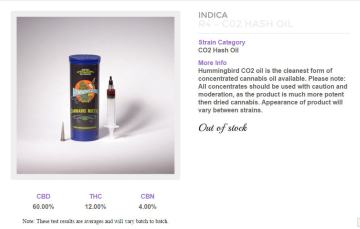
Alternatively, you can buy the oil of your choice and fill the cartridges yourself. This is undoubtedly the way to do it and a wide choice of oils is available, made by CO2 and solvent extraction processes. The Farm, my favourite dispensary in Boulder, is already supplying cannabinoid blends such as a 60% CBD, 12% THC, 4% CBN product which is clearly for medicinal use. I have no doubt that soon we will see a Charlotte’s Web product and Sativex-like blends with equal ratios of THC:CBD. Other, more sophisticated blends of other cannabinoids and probably terpenes will soon follow.
However, I am certain that some propylene glycol is a good thing. The oil vapes much better when diluted and PG is nothing to worry about, it is in many health, cosmetic and food products. It has many uses. It’s a solvent, humectant (keeps things moist), preservative and it helps absorption of some products. It is non-toxic.
There is further development work to be done. I believe there is a ‘sweet spot’ for the correct amount of PG, probably around 20%. I also think the battery and cartridges can be improved, particularly for medical use. Once this is achieved, a product like this with perhaps a 60:40 THC:CBD ratio should form the basis of an application to the Medicines and Health products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) for a marketing authorisation. It will knock Sativex into a cocked hat. In fact, if GW Pharma aren’t investigating this already then they are failing in their duty to shareholders. I shall certainly be doing all I can to research and facilitate the funding to bring such a product to market.
Yes, this is the future of cannabis. Imagine the packaging, marketing and merchandising opportunities for the recreational market. Understand the overwhelming benefits of this as medicine against the raw, herbal product. Yes, I know some will object and the tired old hippy luddites will say it’s a sell out and many more Big Pharma conspiracy theories will emerge but this is the future. Remember you heard it here first.
Channel 4 Drugs Live. How To Cause Confusion About Cannabis.
What is this ‘hash’ that looks like weed and this ‘skunk’ that isn’t cannabis?
Channel 4’s ‘Drugs Live:Cannabis On Trial‘ played fast and loose with facts, terminology and ethical considerations.
To be fair, I greatly enjoyed the programme (well I would wouldn’t I) and there was some fascinating science. Particularly about how the brain responds to music when you’re high and about how CBD protects the ‘salience network’, the key to motivation. This gives weight to the theory of an ‘amotivational syndrome’.
In a week’s time though, all that most of the public will remember is Jon Snow saying that using ‘skunk’ was more terrifying than being in a war zone and his distorted reporting of the recent study by which he implied that 25% of people who use ‘skunk’ will become psychotic.
So I am left with very mixed feelings. The pre-publicity was a disgrace: inaccurate, misleading, unethical – words I have already published and I stand by them.
The brazen misuse of the terms ‘skunk’ and ‘hash’ is an appalling error of judgement by Channel 4, Renegade Pictures and yes, sadly, by two scientists for whom I have the greatest of respect: Professors Val Curran and David Nutt.
Why would you choose to use the same word as the gutter press chooses to demonise cannabis? ‘Skunk’ is a scary word and what it really means is a sativa dominant strain with a modest THC content of 8% and only traces of CBD.
As for hash, it also has a specific meaning: the compressed resin, derived from the plant by sieving or by hand rubbing. By definition a more concentrated form of cannabis, yet the programme claimed exactly the opposite.
A far better, more accurate, more scientific and informative shorthand would have been to describe the cannabis as low CBD, high CBD and placebo.
Surely, whether we agree or disagree with their evidence, we are entitled to expect precision and accuracy from scientists?
The fundamental problem with this programme was that there were no cannabis experts present, only detached academics and scientists or cannabis users who were hardly well informed or articulate. I did of course volunteer but for some reason the producers saw fit to exclude anyone from the cannabis campaign or anyone who has both in depth knowledge and real experience.
Unfortunately, this programme will go the same way as all those other earnest endeavours, ‘The Union’, ‘The Culture High’, ‘In Pot We Trust’, etc – all very enjoyable, self-affirming and satisfying but all preaching to the choir. I’ll be interested to see what the viewing figures were for last night’s programme.
The best bit was David Nutt’s final conclusion. On his scale of harms, even low CBD cannabis (the demon ‘SKUNK’) is less harmful than alcohol, heroin, crack, meth, cocaine, tobacco and speed. After the study he concludes that high CBD cannabis is the least harmful drug of all.
Cannabis Embarrassment At The Home Office
 The re-scheduling of Sativex, the cannabis tincture marketed by GW Pharmaceuticals is causing huge embarrassment at the Home Office.
The re-scheduling of Sativex, the cannabis tincture marketed by GW Pharmaceuticals is causing huge embarrassment at the Home Office.
Everybody’s been able to go along with the white lie up to now that Sativex is some sort of highly complex, super scientific, super medicine containing cannabinoids. True enough, GW Pharma has put millions into development and testing in order to jump through the hoops the government has demanded. At the end of the day though, all Sativex consists of is a tincture, an alcohol extract of herbal cannabis. It’s made simply by gently heating a blend of herbal cannabis in ethanol and then adding a little peppermint oil to taste.
The Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has approved Sativex for the treatment of muscle spasticity in MS. I understand that an approval for the treatment of cancer pain is expected shortly. The problem for the Home Office is that Sativex now has to be re-scheduled under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971. Cannabis is presently in schedule one as having no medicinal value. The Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD) has recommended this week that Sativex be in schedule four, alongside a variety of minor tranquilisers. However, as the ACMD says, “it will not be appropriate to refer to “Sativex”, which is a proprietary name, in any amendment to the misuse of drugs regulations, and that a suitable description of the relevant component(s) of “Sativex” will have to be scheduled.”
This is going to be tough for James Brokenshire to face up to. GW specifies that Sativex contains approximately equal proportions of THC and CBD but that’s not the whole truth. It also contains as many as 400 other chemical compounds which occur naturally in the plant including at least 85 cannabinoids (nobody is exactly sure how many cannabinoids there are or their effects). You see there’s not really any other accurate way of describing Sativex except to call it cannabis. So how can Mr Brokenshire possibly move it to schedule four? He endlessly repeats the propaganda that “there are no medicinal benefits in cannabis”.
Either Mr Brokenshire has to come clean and accept that his past position was incorrect or he has to promote some further deception.
I trust he will prove to be an honourable man.
Cannabis And Cannabinoids: Pharmacology, Medicalization And Recreational Use

By Professor Roger Pertwee
Discovery of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol
Cannabis has been used as a medicine, for religious ceremonies and recreationally for over 5000 years. Indeed, an alcohol-containing tincture of cannabis (Figure 1) was a licensed medicine in the UK until its withdrawal in the early 1970’s.
In contrast, the discovery that cannabis contains (–)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and that many of the effects experienced when cannabis is taken recreationally are caused by this ‘phytocannabinoid’ was made less than 100 years ago (Pertwee, 2006). These effects include altered mood (usually euphoria); altered perception such that colours seem brighter, music more pleasant and ‘felt time’ appears to pass more slowly than ‘clock time’; an increased desire for sweet food (the ‘munchies’); changes in thought processes; impaired memory…and eventual drowsiness. They can also include increased heart rate, a lowering of blood pressure resulting in dizziness and, at high doses, hallucinations and feelings of paranoia. There is good evidence too that Δ9-THC targets the reward centres of the brain in a manner that can lead to psychological dependence, and that abrupt termination of repeated use of cannabis or Δ9-THC can trigger a transient physical withdrawal syndrome that in abstaining recreational cannabis users most commonly includes disturbed sleep, reduced appetite, restlessness, irritability, sweating, chills, a feverish feeling and nausea.
Some Cannabinoid Pharmacology
The discovery of Δ9-THC was followed by the development of synthetic compounds capable of inducing Δ9-THC-like effects. Results obtained from pharmacological research with some of these compounds culminated in the discovery that they produce many of their central effects by activating specific sites on nerve terminals called cannabinoid CB1 receptors in a manner that influences the normal functioning of the brain (Pertwee, 2006). This finding prompted a search for molecules within our own bodies that can activate these receptors and, in 1992, led to a second major discovery – that we do indeed produce and release such molecules. The first of these ‘endocannabinoids’ to be identified was an ethanolamide of the omega-6 unsaturated fatty acid, arachidonic acid. It was named
‘anandamide’, ananda being the Sanskrit word for internal bliss. It has subsequently emerged that there is at least one other cannabinoid receptor (CB2), that there are other endocannabinoids, and that this ‘endocannabinoid system’ of receptors and endogenous receptor activators plays major roles in the control of our health and in ameliorating unwanted symptoms such as pain.
The search is now on for additional cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoids. Indeed, we have obtained evidence that ethanolamides, which are converted in our bodies from omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids that are found, for example, in fish oil, can both activate cannabinoid receptors and attack cancer cells (Brown et al., 2010).
The Medicalization Of Cannabinoids
Individual cannabinoids first entered the clinic in the 1980’s (Crowther et al., 2010). The first of these was Nabilone (Cesamet), a synthetic Δ9-THC-like compound that is used to suppress nausea and vomiting produced by cancer chemotherapy. Synthetic Δ9-THC (Marinol) was licensed soon after Nabilone for the same purpose, and subsequently as an appetite stimulant, particularly for AIDS patients. Nabilone
and Marinol were recently joined in the clinic by Sativex: in Canada (2005) for the relief of multiple sclerosis and cancer pain and in the UK (2010) to treat spasticity due to multiple sclerosis. Sativex has also received regulatory authorisation in Spain. Its main constituents are two phytocannabinoids, Δ9-THC and cannabidiol, both extracted from cannabis.
Importantly, whereas exogenously administered cannabis and individual cannabinoids such as Δ9-THC and Nabilone target all cannabinoid receptors in the body and so ‘flood’ the whole endocannabinoid system, endocannabinoids released endogenously are somewhat more selective since they seem to be released in a manner that only targets subpopulations of their receptors. Although such release is often ‘autoprotective’ it can sometimes be ‘autoimpairing’, leading for example to CB1 receptor-mediated obesity. There is, however, currently little interest in developing medicines from compounds that block CB1 receptors, as such a blockade could well also suppress CB1 receptor-mediated autoprotection. Indeed, the CB1 receptor blocking drug, Rimonabant, was recently withdrawn from the clinic because of an increased incidence of depression and suicidality in patients taking it as an anti-obesity agent.
The fact that Cesamet, Marinol and Sativex are all in the clinic is of course an indication that, as prescribed, these medicines do significantly more good than harm. Even so, there is considerable interest in developing a second generation of cannabinoid medicines that display even greater ‘benefit-torisk ratios’ (Pertwee, 2009). Possibilities include compounds that avoid the production of unwanted cannabinoid CB1 receptor-mediated effects by:
(1) Only activating cannabinoid receptors that are located outside the brain and spinal cord.
(2) Only activating cannabinoid receptors in particular tissues such as skin or spinal cord by being administered directly into these tissues.
(3) Activating cannabinoid CB2 but not cannabinoid CB1 receptors.
(4) Being administered at low doses that produce a cannabinoid receptor-mediated enhancement of the sought after effects of non-cannabinoid medicines but are insufficient to produce significant cannabinoid receptor-mediated unwanted side effects.
(5) Boosting the levels of endocannabinoids when these are being released in an ‘autoprotective’ manner, for example to relieve pain.
(6) Targeting ‘allosteric’ sites that we have discovered to be present on cannabinoid CB1 receptors in a manner that will boost the ability of autoprotectively released endocannabinoids to activate these receptors.
Cannabis: A Complex Scenario
Δ9-THC is synthesized in the cannabis plant from a nonpsychoactive precursor, Δ9-THC acid. This process can be greatly accelerated by heat which is why cannabis is usually smoked, often with tobacco, consumed in preheated food or inhaled from ‘volcano’ vaporizers that create fumes by heating cannabis without burning it or producing smoke. Other pharmacologically active phytocannabinoids can also be
formed from their acids by heating cannabis. These include the non-psychoactive yet pharmacologically active compounds, cannabidiol (CBD), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (Δ9-THCV) and cannabigerol (CBG), each of which has actual (CBD) or potential medical applications. Some of these phytocannabinoids are really ‘fighto’ cannabinoids, their presence in cannabis making it a pharmacological ‘battlefield’. Thus
we have discovered that although CB1 receptors are activated by Δ9-THC, they can be blocked by Δ9-THCV. It has also been found that CBD can oppose certain effects produced by cannabis or Δ9-THC. Indeed, whilst there is evidence that the presence of Δ9-THC in cannabis increases the risk of developing schizophrenia for certain individuals, there is also strong evidence that cannabidiol is a potential medicine for the treatment of schizophrenia. A further complication is that the relative concentrations of different phytocannabinoids are not the same in all strains of cannabis, in all parts of the same cannabis plant or in male and femalecannabis plants, the female flowering heads of sinsemilla (‘without seeds’) being particularly rich in Δ9-THC. This may have important consequences for those who take cannabis either recreationally or for the quite different purpose of self-medication, as high CBD:THC or THCV:THC ratios may lessen the risk from cannabis of developing schizophrenia or cannabis dependence…although probably also alter the perceived nature of a cannabis-induced ‘high’.
Spice
One notable recent event has been the arrival in the recreational cannabis world of herbal mixtures laced with synthetic cannabinoids (‘designer drugs’) such as JWH-018 (e.g. Spice or K2, named after the second highest mountain on earth). These little-investigated synthetic cannabinoids share the ability of Δ9-THC to activate cannabinoid CB1 receptors and hence to produce a ‘high’. Moreover, any of them that
activate these receptors more strongly than Δ9-THC will most likely produce a more intense ‘high’ and perhaps also more serious unwanted effects than usually experienced by recreational cannabis users. They probably also differ from THC in other ways. Thus, although Δ9-THC shares its ability to target cannabinoid receptors with many synthetic compounds, the additional pharmacological actions it possesses provide it with a unique ‘pharmacological fingerprint’ that distinguishes it from many of these other compounds.
Harm Minimization For Recreational Cannabis
One important challenge for the International Narcotics Control Board that monitors and implements United Nations drug control conventions is to select an optimal but workable strategy for minimizing the harm that is now being caused both to themselves and to Society by some of the many millions of people world-wide who currently take cannabis (or Spice) recreationally and also, indeed, by some of those who self-medicate with ‘street’ cannabis. For the UK, options include leaving the present law unchanged and increasing or
decreasing current penalties for the supply and/or possession of ‘street’ cannabis. It would also be advisable to develop strategies directed (i) at discouraging cannabis from being taken by adolescents or other individuals who are thought to be at particular risk from cannabis-induced harm and (ii) at providing advice (a) about combinations and levels of cannabinoids in cannabis that are thought to be the least
harmful and (b) about how to take cannabis as an inhaled unburnt vapour or in other ways that avoid the lung damage caused by smoked cannabis. It will be important that policy makers have discussions with cannabinoid pharmacologists whilst considering these and any other potential strategies for minimizing the harm caused by recreational cannabis.
Brown I, Cascio MG, Wahle KWJ, Smoum R, Mechoulam R, Ross RA, Pertwee RG and Heys SD. Cannabinoid receptor dependent and independent anti-proliferative effects of omega-3 ethanolamides in androgen receptor positive and negative prostate cancer cell lines.
Carcinogenesis 2010; 31: 1584-1591.
Crowther, SM, Reynolds, LA and Tansey, EM (eds). The Medicalization of Cannabis. Witness Seminar Transcript. Volume 40. The Wellcome Trust Centre for the History of Medicine, at UCL. 2010; http://www.ucl.ac.uk/histmed/downloads/c20th_group Pertwee RG. Cannabinoid pharmacology: the first 66 years. Br J Pharmacol 2006; 147: S163-S171. Pertwee RG. Emerging strategies for exploiting cannabinoid receptor agonists as medicines. Br J Pharmacol 2009; 156: 397-411. Professor Roger Pertwee has three degrees from the University of Oxford: MA (in biochemistry), D.Phil. (in pharmacology) and D.Sc. (in physiological sciences). He is Professor of Neuropharmacology at the University of Aberdeen, Director of Pharmacology for GW Pharmaceuticals, co-chairman of the International Union of Pharmacology (IUPHAR) Subcommittee on Cannabinoid Receptors, a co-ordinator of the British Pharmacological Society’s Special Interest Group on Cannabinoids and visiting Professor at the University of Hertfordshire. He has also served as chairman of the International Association for Cannabis as Medicine (IACM; 2005-2007) and as President of the International Cannabinoid Research Society (ICRS; 2007-2008; 1997-1998) and is currently ICRS International Secretary and a member of the IACM board of directors. He was the recipient of the 2002 Mechoulam Award “for his outstanding contributions to cannabinoid research” and in 2005 was recognized to be an “ISI Highly Cited Researcher” and hence among “the world’s most cited and influential researchers” (see Pertwee at http://isihighlycited.com/). His research has focused mainly on the pharmacology of cannabinoids. This he began in 1968 at Oxford University and continued when he moved to Aberdeen in 1974. His research has played major roles in:
• the discovery of endocannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system;
• the recent discovery that ethanolamides formed from omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids seem to be endocannabinoids;
• the gathering of evidence supporting cannabinoids for the management of multiple sclerosis;
• the discovery that tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is a phytocannabinoid;
• the pharmacological characterization of certain phytocannabinoids and of novel synthetic cannabinoids, e.g. the phytocannabinoids THCV, cannabidiol and cannabigerol, the first water-soluble cannabinoid (O-1057), the first CB1 receptorselective agonists (e.g. methanandamide), and a widely-used CB2 receptor antagonist (AM630);
• the discovery of a cannabinoid CB1 receptor allosteric site;
• the development of cannabinoid bioassays, some widely used (e.g. the “ring test”).
See also www.abdn.ac.uk/ims/staff/details.php?id=rgp
The Truth About Sativex
 Sativex is super strong, concentrated cannabis. Nothing more, nothing less.
Sativex is super strong, concentrated cannabis. Nothing more, nothing less.
GW Pharmaceuticals would have you believe that it’s a “pharmaceutical” product because according to its research that’s what patients prefer. As the GW spokesman puts it, “It’s a pharmaceutical solution, formulated with the ability to deliver a precise dose and with stringent standards of quality, safety and efficacy”.
 In fact, what GW does is grow high quality cannabis under pretty much the same conditions as most illegal growers. It uses clonal propagation to ensure consistent levels of cannabinoids. Lighting and hydroponic nutrition is computer controlled with automatic ventilation. It really is no different from the most sophisticated and efficent illegal cannabis farms. It’s a recognised and proven technology now also used by Bedrocan in Holland, the Dutch government’s exclusive medicinal cannabis grower and Gropech in California which is building a new 60,000 sq ft facility in Oakland for a crop worth $50 million per year.
In fact, what GW does is grow high quality cannabis under pretty much the same conditions as most illegal growers. It uses clonal propagation to ensure consistent levels of cannabinoids. Lighting and hydroponic nutrition is computer controlled with automatic ventilation. It really is no different from the most sophisticated and efficent illegal cannabis farms. It’s a recognised and proven technology now also used by Bedrocan in Holland, the Dutch government’s exclusive medicinal cannabis grower and Gropech in California which is building a new 60,000 sq ft facility in Oakland for a crop worth $50 million per year.
The difference between these crops from legal and illegal growers is insignificant. It’s similar to buying your tomatoes from the supermarket or the farm shop.
GW takes its high quality cannabis, chops it up and makes a tincture by heating it under pressure with CO2 and then adding ethanol to precipitate an oil. Then, with the addition of a little peppermint oil to mask the taste and some preservative, the filtered liquid is packaged into tiny little aerosol bottles. Each spray delivers 2.7mg of THC and 2.5mg of CBD. What GW doesn’t tell you that it also contains all the other 100+ cannabinoids found in the plant, each of which has its own mechanism of action and effect. It also contains flavonoids, terpines and other compounds. Everything that is found in the plant.
I applaud GW Pharmaceuticals for bringing the enormous benefits of cannabinoid therapy into the 21st century. It’s nothing new though. The medicinal value of the plant has been known and widely used for thousands of years. Only in the last century has it been demonised by lies and propaganda. It would be a mistake though to think that Sativex is anything different from the plant itself. It’s just been wrapped up in a marketing and physical package which has enabled stupid and cowardly politicians to accept it.
In fact, Sativex remains just as illegal in Britain as herbal cannabis. Even though it has received MHRA approval for use in the treatment of MS spasticity and may be prescribed by a doctor, it remains a schedule 1 drug under the Misuse Of Drugs Act. The Home Office has indicated that it intends to amend the law but has not yet done so. This means that any pharmacist who dispenses Sativex at present is guilty of exactly the same criminal offence as any street dealer in weed or hash.
The Home Office will, of course, turn a blind eye to this but not to medicinal herbal cannabis even though, in every sense, it is identical to Sativex (except that Sativex also contains alcohol and peppermint oil). The stark idiocy of British law is revealed.
Never before has there been a better example of the how the law is an ass and so are the spineless politicians who support it.